We compiled the most frequently asked questions in the following Q&A format.
Click on a question to display each Q&A page.
- Q1 How are radiation screenings on farm products carried out?
- Q2 What items are targeted for monitoring?
- Q3 How is the reference level for radioactive substances in farm products set?
- Q4 Are nuclides other than radiocesium inspected?
- Q5 In monitoring up until now, how much farm products exceeded the reference level?
- Q6 Are farm products exceeding the reference level distributed?
- Q7 Are farm products below the reference level really safe?
- Q8 How are distribution restrictions established and cancelled based on monitoring results?
- Q9 What is the difference between distribution restrictions and voluntarily distribution restraints?
- Q10 How are "harvest" "consumption" and "distribution" different in terms of voluntarily distribution restraints and distribution restrictions?
- Q11 Presently, what farm products are under distribution restraints or consumption restrictions?
- Q12 Regarding vegetables that cannot be distributed, are there any problems with personal consumption?
1.How are radiation screenings on farm products carried out?

In Fukushima Prefecture, a system for testing radiation in farm products to ensure safe distribution and consumption is set in place where environmental radiation of agricultural, forestry and marine products are monitored in times of emergency under national guidelines, as well as voluntary inspections conducted by producers at production centers including but not limited to inspections on all gross quantity bags of rice.
Emergency environmental radiation monitoring on agriculture, forestry and marine products are carried out in all affected cities and prefectures, including Fukushima and is based on " concepts of inspection, planning and the establishment and cancellation of items and areas to which the restrictions of distribution and/or the consumption of foods concerned applies " that the Nuclear Emergency Response Headquarters (General manager: Prime Minister) of the national government established.
Based on these guidelines, the prefecture establishes sampling plans and performs sample extractions/measurements.
Monitoring results are available on the prefecture's homepage and also released to the press.
Related links
(Monitoring Results)
- Monitoring results of agricultural, forestry and fishery products from Fukushima Prefecture
- Site for New Fukushima Agriculture, forestry and marine products monitoring information (Fukushima Prefecture)
(Voluntary inspection results)
- Information on inspection of all gross quantity bags for Fukushima-made rice (Fukushima Prefecture Crop Production Division) [Japanese Only]
- Inspection information of radioactive substances within crops/bounty in Fukushima (Fukushima Association for Securing Safety of Agricultural Products)
- Examination for Ampo persimmon information (JA National Peasant Union Fukushima) [Japanese Only]
2.What items are targeted for monitoring?

The prefecture monitors all agriculture, forestry and marine products produced and harvested within Fukushima Prefecture purposed for distribution and sale.
In FY2017, we carried out targeting at grains, vegetables, fruit, livestock products, 519 items including marine product.
Note: The number of the items according to food group and the number of inspection (FY 2017)
| Food group | Number of items | Number of inspections | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grains | ※Brown rice | 1 | 5 |
| Other grains | 13 | 433 | |
| Vegetables, fruit | 255 | 2,855 | |
| Livestock products | Raw milk | 1 | 398 |
| Meat | 5 | 3,578 | |
| hen's egg | 1 | 111 | |
| Pasture grass, feed crop | - | 680 | |
| Marine products | 178 | 9,288 | |
| Wild vegetables, mushrooms | 61 | 2,111 | |
| Other | 4 | 86 | |
| Total | 519 | 19,545 | |
※The number of brown rice inspections are the results of detailed inspections.
Related links
3.How is the reference level for radioactive substances in farm products set?

The Food Sanitation Act establishes the reference level for radioactive materials found in food including farm products where if one were to continue eating these products throughout one's life, the result of consuming products with radioactive materials are sufficiently small and at a safe enough level (1mSv a year or less) to not cause any health problems.
The reference level for radiocesium in "drinking water" "milk" "baby food" and "general food" are each set based on their consumption quantity.
The Limits on radioactive materials in foods : Reference Levels
| Categories | Limit (Bq/kg) |
|---|---|
| Drinking water | 10 |
| Milk | 50 |
| General Foods | 100 |
| Infant Foods | 50 |
Related links
4.Are nuclides other than radiocesium inspected?

Although the reference level set by the government targeting food including agricultural products was established to detect cesium, the main substance released from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, all nuclides with a longevity greater than half a year are also included in the reference level.
With consideration to contribution ratios, the reference level for radiocesium are decided beforehand with leeway so that additional radiation exposure does not exceed 1mSv a year even if other nuclides get into food such as farm products.
Related links
5.In monitoring up until now, how much farm products exceeded the reference level?

We had 10 (0.05% of the whole) standard value excess in FY2017.
FY2013: 419 cases (1.5% on the whole), FY2014: 113 cases (0.4% on the whole), FY2015: 18 cases (0.08% on the whole), FY2016: 6 cases (0.03% on the whole). Basically, those real numbers and ratios are on a downward trend.
Number of emergency environmental radiation monitoring of agriculture, forestry and marine products
| FY2014 | FY2015 | FY2016 | FY2017 | |||||
| Number of inspections | Cases where reference level exceeded | Number of inspections | Cases where reference level exceeded | Number of inspections | Cases where reference level exceeded | Number of inspections | Cases where reference level exceeded | |
| ※Brown rice | 2 | 0 | 9 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Grains (Excl. Brown rice) | 2,473 | 2 | 2,724 | 2 | 705 | 0 | 433 | 0 |
| Vegetables, fruit | 5,850 | 0 | 4,585 | 0 | 3,793 | 0 | 2,855 | 1(*1) |
| Raw milk | 408 | 0 | 413 | 0 | 415 | 0 | 398 | 0 |
| Meat | 4,319 | 0 | 3,969 | 0 | 3,791 | 0 | 3,578 | 0 |
| hen's egg | 140 | 0 | 144 | 0 | 143 | 0 | 111 | 0 |
| Pasture grass, feed crop | 1,527 | 11 | 1,148 | 0 | 922 | 0 | 680 | 0 |
| Marine products | 9,688 | 75 | 9,215 | 7 | 9,505 | 4 | 9,288 | 8 |
| Wild vegetables, mushrooms | 1,564 | 25 | 1,562 | 7 | 1,832 | 2 | 2,111 | 1 |
| Other | 70 | 0 | 86 | 0 | 74 | 0 | 86 | 0 |
| Total | 26,041 | 113 | 23,855 | 18 | 21,180 | 6 | 19,545 | 10 |
※The number of brown rice inspections are the results of detailed inspections.
*1 Chestnuts from the designated sites (not distributed in the market since October 2012).
6.Are farm products exceeding the reference level distributed?

Based on the Special Measures for Nuclear Disaster Act and the Food Sanitation Act, production centers (communities, and former municipalities. Regarding marine products, sea areas, swamps, and rivers) with items that exceeded the reference level for radioactive substances in food products are ordered to be placed under distribution restrictions by the government or a voluntary restriction is placed by the prefecture as a whole. Items falling under these production centers are never distributed.
7.Are farm products below the reference level really safe?

The current reference level, established by the national government, is made to be at an adequate level where effects of continued consumption of radioactive material found in agricultural products are small and safe (1mSv a year or less).
It has been said that there is not enough information on the dangers of exposure to low levels of radiation. However, low levels of radiation within 100 mSv are thought to be so small that the effects can not be verified scientifically.
Related links
- Measures against radioactive contamination of food caused by the accident (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare)
- Response to the Great East Japan Earthquake (Oct. 2012) (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare)
- Information related to the Great East Japan Earthquake FAQ (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare) [Japanese Only]
8.How are distribution restrictions established and cancelled based on monitoring results?

In cases where monitoring results show that agricultural products containing radiocesium exceed the reference level, the prefecture will immediately request the municipality be placed under a voluntary distribution restraint.
Afterwards, additional inspections are performed on the applicable items within the production centers and to outlying areas with voluntary distribution restraints. The government (Nuclear Emergency Response Headquarters) will determine necessary distribution restrictions and assess the questioned area.
When lifting restrictions, for example in the case of vegetables, in one municipality three or more areas are subjected to radiocesium inspections and fixed inspections are conducted on every item.
Restrictions are lifted if within the most recent month inspection results are below the reference level and when predictions can be made stating results exceeding the reference level will not appear.
Flowchart from Monitoring to Lifting of Restrictions
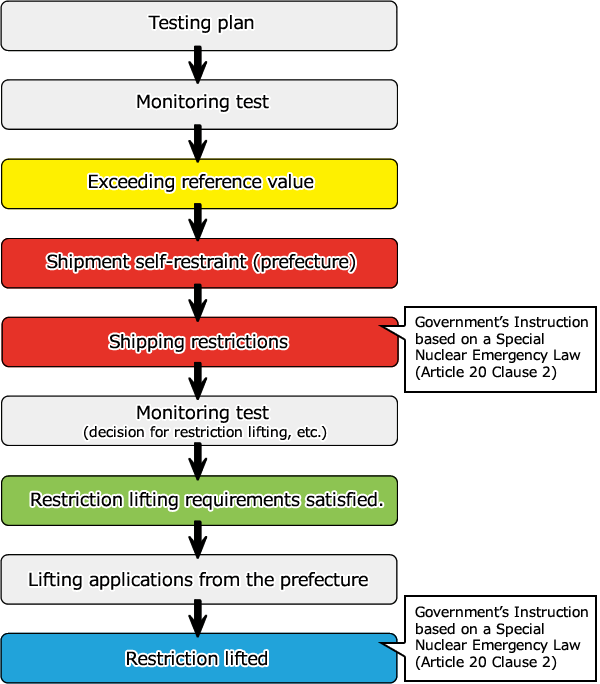
Based on: "Considerations regarding the implementation and lifting of the items and areas subjected to the inspection plan and the shipment restrictions" (revision released by the Nuclear Emergency Response Headquarters, March 20, 2015)
9.What is the difference between distribution restrictions and voluntarily distribution restraints?

Distribution restrictions are instructions dependent on the national government (Nuclear Emergency Response Headquarters) and voluntarily refraining distribution restraints are requests dependent on the prefectural governor.
In such cases where monitoring results conducted by the prefecture illustrate agricultural products containing an exceeded level of radiocesium the prefecture immediately requests that the municipality producing these products be placed under voluntarily distribution restraints.
In production centers and outlying areas where restraints were called for, the national government (Nuclear Emergency Response Headquarters) confirms detection circumstances of concerned items and necessary distribution restrictions while also passing decisions on the questioned area.
10.How are "harvest" "consumption" and "distribution" different in terms of voluntarily distribution restraints and distribution restrictions?

- Voluntary restraints on harvesting
- The prefecture requests that vegetables, fruit and some types of grains be voluntarily restrained.
Regardless of intention for sale, distribution or personal use the prefecture desires that harvests of applicable items be voluntarily restrained. - Voluntary restraints on fish harvesting
- Prefecture requests that some classes of fish (freshwater fish) found in inland fisheries be voluntarily
restrained.
The prefecture desires that marine harvesting techniques including angling be voluntarily restrained. - Consumption restrictions
- The national government has restricted vegetables and certain types of mushrooms.
There are restrictions in consumption (eating) of foods such as certain types of wild mushrooms.
- Distribution restrictions
- Instructions for restrictions and requests for voluntarily distribution restraints are carried out by the national
government or the prefecture.
In addition, distribution with intention to sell at markets, direct sale offices or to give out free of charge are all labeled as "distribution".
11.Presently, what farm products are under distribution restraints or consumption restrictions?

Farm products that have requests to be refrained from consumption and/or distribution reflect monitoring results which are frequently updated.
We publish information on our home page about farm products in Fukushima prefecture that have restrictions/restraints on them.
Please refer to the link below concerning items/food products or production centers that have been requested to refrain from consumption or distribution.
12.Regarding vegetables that cannot be distributed, are there any problems with personal consumption?

We do not recommend consumption of vegetables with distribution restrictions.
In addition, we also provide basic inspections to detect radioactive substances within vegetables wanted to be consumed personally. For details, please contact your municipality in Fukushima Prfecture.