See here for the latest information
Information on various monitoring inspections and other surveys in Fukushima Prefecture
"~Fukushima Today~Steps for Reconstruction and Revitalization in Fukushima Prefecture"
Standard Limits of Radioactive Substances for Food in Japan
Under the Food Sanitation Act, the standard limits were established and enforced on April 1, 2012.
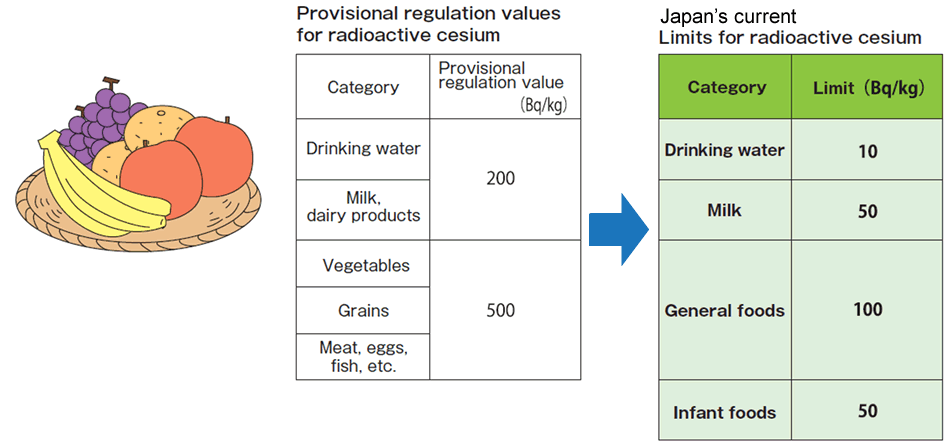
(Quotation: Consumer Affairs Agency, Government of Japan)
Overseas indexes concerning radioactive substances in food(Bq/kg)
| Radionuclides | Japan | Codex Alimentarius Commission | EU | US |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radioactive cesium | Drinking water...10 | Drinking water...1,000 | All food...1,200 | |
| Milk...50 | Milk...1,000 | |||
| Infant food...50 | Infant food...1,000 | Infant food...400 | ||
| General food...100 | General food...1,000 | General food...1,250 | ||
| Upper limit value of additional dose | 1mSv | 1mSv | 1mSv | 5mSv |
| Estimated values of the proportion of food containing radioactive substances | 50% | 10% | 10% | 30% |
It is not possible to simply compare the numerical values because the reference values (standard limits) were established by taking into account the estimated impact of the amount of food ingested, the proportion of food containing radioactive substances, etc. The Codex Alimentarius Commission, EU, and Japan have designated the upper limit of additional doses as being 1 mSv/year.
 |
Source: "Food and Radiation Q&A," issued by the Consumer Affairs Agency (Japanese: March 2018) |
 |
Establishment of the limits for Radionuclide in Foods (MHLW)
1. Concept of Japanese limits
The limits are based on 1 mSv in a year as an intervention level for the following reasons;
- The Guideline Levels of Codex Alimentarius (CODEX STAN 193-1995) adopted 1 mSv in a year as an intervention exemption level.
- Monitoring surveys demonstrated that concentrations of radionuclide decreased in most foods as time goes by (ALARA principle, As Low As Reasonably Achievable).
2. Comparison between Japanese limits and the Codex guideline levels
Japanese limits for radioactive cesium
| Category | Limit(Unit:Bq/kg) |
|---|---|
| Drinking water | 10 |
| Milk | 50 |
| General Foods | 100 |
| Infant Foods | 50 |
Codex guideline levels for radioactive cesium
| Category | Limit(Unit:Bq/kg) |
|---|---|
| Infant foods | 1000 |
| Other foods | 1000 |
- The Codex guideline adopts 10% as the ratio of the amount of foodstuff imported from contaminated areas; on the other hand Japan established the limits on the assumption that 50% of the marketed foods are contaminated, based on Japan’s food self-sufficiency.
- Japanese limits for radioactive cesium take into account the contribution of radioactive strontium, plutonium etc.
- Japanese limits are calculated taking age-category into consideration.